
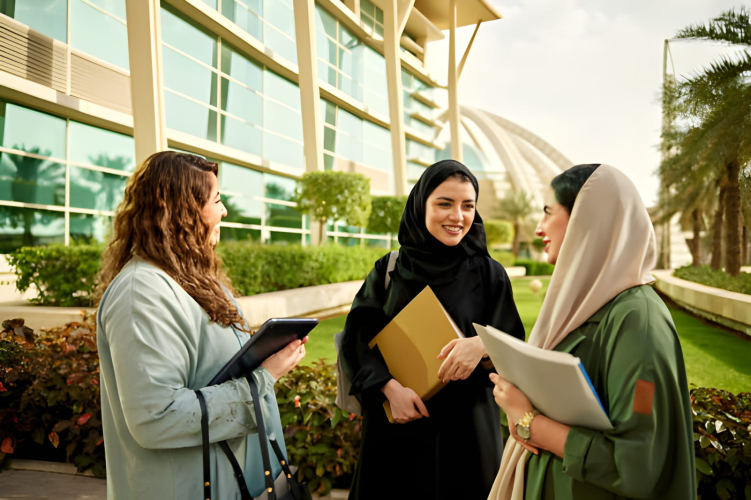
Happy International Women’s Day
On 8 March, we proudly celebrate International Women’s Day with our NAPS community.
At NAPS, our students come from all around the world, bringing different cultures, stories, and dreams. As international students, many of you have travelled far from home, faced new challenges, adapted to a new environment, and continued working toward your goals.
That courage and determination deserve to be recognised and celebrated.
International Women’s Day is not only about celebrating achievements, but also about supporting each other, building confidence, and creating opportunities for women in education, careers, and leadership. Over the years, we have seen more women becoming leaders in business, government, education, and technology. Since the 1990s, social attitudes toward women have changed significantly. More women now pursue higher education, lead organisations, start businesses, and speak openly about equality, inclusion, and respect. Although challenges still exist, the progress made from 1990 to 2026 shows how strong voices, education, and global collaboration can create meaningful change for women around the world.
Our female students are future professionals, innovators, and leaders who will contribute to communities across many countries.
For more information about the day, please visit https://www.internationalwomensday.com/
Happy International Women’s Day to all our amazing NAPS students.

MBA Program Sydney: CRICOS Approved Business Degree at NAPS
When choosing to pursue a business degree in Australia, discerning students look for more than just classroom learning—they seek qualifications that deliver global recognition, real-world impact, and career mobility. The MBA program at the National Academy of Professional Studies (NAPS) in Sydney stands out not only for its rigorous curriculum, but also for its coveted CRICOS approval, ensuring that international students gain a degree acknowledged throughout Australia and far beyond.
Why CRICOS Approval Matters
CRICOS (Commonwealth Register of Institutions and Courses for Overseas Students) approval is a pivotal indicator of quality and compliance in Australia’s education sector. MBA programs with this designation, such as NAPS’s, are specifically tailored for international students, delivering education that meets strict standards for teaching, facilities, and support services.
A CRICOS-approved MBA signals to employers and global institutions that your degree adheres to the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF)—a benchmark for advanced business acumen and managerial skills instantly recognized worldwide. International graduates from such programs not only fulfil visa requirements, but also position themselves as strong contenders in competitive job markets.
NAPS MBA: Curriculum Built for Modern Leaders
The MBA program at NAPS is structured to cultivate visionary leaders who excel in dynamic, interconnected economies. Unlike generic business degrees, the NAPS curriculum seamlessly integrates theory with hands-on applications. Topics span strategic management, global marketing, innovation, ethics, and digital transformation—areas central to today’s business success.
What truly sets NAPS apart is the emphasis on soft skills and real-world leadership. Group projects, case studies, and industry simulations foster decision-making, negotiation, and critical thinking. Students engage in networking sessions and live projects with corporate partners to ensure they graduate ready not just for the boardroom, but for global change.
World-Class Sydney Campus Experience
Sydney is more than a world-class city—it’s a thriving business hub where cultures, sectors, and ideas intersect. NAPS’s campus in central Sydney gives MBA candidates direct access to Australia’s top employers, entrepreneurial events, and industry mentors. Students benefit from modern facilities, collaborative learning spaces, and a vibrant multicultural student body that reflects the broader business landscape of New South Wales and the Asia-Pacific.
Pathways to Career Success
Graduates of the NAPS MBA are equipped to lead in consulting, multinational corporations, government, and emerging tech startups. The CRICOS-approved degree is recognized by professional bodies, bolstering eligibility for positions that require advanced business qualification, project management expertise, and strategic vision.
NAPS’s extensive career support—including interview coaching, CV workshops, and networking introductions—ensures MBA graduates enter the workforce with confidence. Many alumni report faster promotions, superior mobility between global markets, and successful transitions into executive roles both in Australia and internationally.
The NAPS Edge: Industry Engagement and International Recognition
Not only do NAPS MBA students learn from academics with global consulting experience, but they also interact with professionals through partnerships and events. Industry input shapes coursework, keeping graduates ahead of trends in digital business, finance, ethical leadership, and cross-border management.
International students, in particular, praise the welcoming, supportive atmosphere that helps them adapt and thrive in Sydney’s cosmopolitan business environment.
How to Join NAPS’s MBA Program
The admission requirements for prospective candidates include meeting specific academic and English language criteria. However, the admissions team provides personalized guidance to help applicants through every step of the process. With multiple intakes offered throughout the year, students can choose flexible start dates and complete their studies at a pace that best supports their career goals.
Applying is straightforward: Submit your academic transcripts, proof of English proficiency, and a detailed resume. Interviews and references can further reinforce your fit for advanced business study at NAPS.
Why Should You Consider NAPS for Your MBA?
Choosing the right institution for your MBA can shape your professional future — and that’s where NAPS stands out. Here’s why pursuing your MBA at NAPS could be one of the most rewarding decisions for your career.
- CRICOS approved for global recognition
- Located in Sydney, a leading international business city
- World-class faculty and innovative curriculum
- Strong industry connections and project-based learning
- Dedicated support for international students
- Proven graduate outcomes in leadership and growth
In the crowded field of MBA education, the NAPS offering in Sydney is not just another business degree—it’s a launchpad for leaders ready to make an impact across industries and continents.
Ready to take the next step in your international business career? Contact NAPS today to learn how their CRICOS-approved MBA program can unlock your leadership potential and global opportunities.

Master of Information Technology Sydney: Build a Future-Ready Tech Career at NAPS
In a world where technology drives innovation across every industry, the demand for skilled IT professionals continues to soar. The Master of Information Technology (MIT) program at the National Academy of Professional Studies (NAPS) in Sydney equips students with advanced technical expertise, problem-solving ability, and global career readiness — preparing them to thrive in today’s fast-evolving digital world.
Why Choose a Master of Information Technology in 2025
Technology lies at the heart of every business transformation. From artificial intelligence and cloud computing to cybersecurity and big data, IT professionals are shaping the future of how organizations operate. Pursuing a Master of Information Technology positions you at the forefront of this global digital revolution.
In Australia, the IT sector continues to grow rapidly, creating thousands of new jobs each year. Graduates with advanced IT qualifications enjoy high employability, strong earning potential, and the flexibility to work across diverse industries — from finance and healthcare to software development and consulting.
Master of Information Technology at NAPS: Advanced, Practical, and Globally Relevant
The NAPS Master of Information Technology program blends academic rigor with real-world application. Designed with input from industry professionals, it equips students with both the technical and strategic skills employers value most.
Students gain in-depth knowledge across:
- Software engineering and application development
- Data analytics and database systems
- Cloud computing and virtualization
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Cybersecurity and network management
- IT project management and enterprise systems
With hands-on labs, industry simulations, and project-based learning, NAPS ensures that graduates can apply their knowledge effectively to real business challenges.
What Makes the NAPS Master of Information Technology Stand Out
NAPS offers a unique blend of academic excellence and industry relevance, preparing students for success in competitive IT environments.
- Industry-Linked Curriculum: Every subject is aligned with current technology standards, ensuring graduates possess practical, up-to-date expertise.
- Flexible Learning Options: With multiple intakes throughout the year, NAPS allows students to start when it suits them best — whether studying full-time or part-time.
- Real-World Experience: Students engage in capstone projects, internships, and networking events, building valuable industry connections before graduation.
- Personalized Support: From application to career preparation, NAPS provides dedicated academic and career guidance every step of the way.
Career Outcomes After the Master of Information Technology
Graduates of the NAPS Master of Information Technology program are equipped for diverse, high-growth roles such as:
- IT Manager
- Software Engineer
- Data Analyst / Data Scientist
- Network Engineer
- Cloud Solutions Architect
- Cybersecurity Specialist
- IT Project Manager
- AI / Machine Learning Engineer
With Australia’s growing digital economy and ongoing investment in innovation, NAPS MIT graduates are in demand across multiple industries — both locally and internationally.
Future-Focused and Industry-Ready
As technology evolves, so does the NAPS Master of Information Technology curriculum. Students explore emerging trends like AI integration, blockchain innovation, cloud migration, and data ethics, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve and future-ready for tomorrow’s IT challenges.
Why Choose NAPS for Your Master of Information Technology
Choosing NAPS means choosing a university that connects learning with career outcomes.
- Industry-driven curriculum and practical project work
- Experienced faculty with global IT expertise
- Access to cutting-edge labs and innovation spaces
- Career support including resume workshops and employer introductions
- Flexible study schedules for domestic and international students
- Growing alumni network in Australia’s tech and business sectors
Conclusion: Your Future in IT Starts Here
The future belongs to those who can innovate with technology — and the Master of Information Technology at NAPS gives you the skills, confidence, and global outlook to lead that future. Whether you’re advancing your career or entering the IT field for the first time, NAPS provides the platform to turn your ambition into achievement.
Take the Next Step
Ready to build your career in technology? Apply now to the Master of Information Technology at NAPS Sydney and join a community of innovators shaping the future of the digital world.

Master Professional Accounting: Fast Track to CPA
The accounting profession in Australia is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand for qualified professionals reaching new heights in 2025. For ambitious individuals seeking a direct pathway to becoming a Certified Practising Accountant (CPA), the Master of Professional Accounting stands as the most strategic educational investment available today.
Australia's robust economy and complex regulatory environment have created an insatiable appetite for skilled accounting professionals. Recent data shows accounting positions are expected to grow strongly over the next five years, with salaries for qualified CPAs averaging $85,000-$120,000 annually for mid-level professionals. This demand isn't just local – Australian accounting qualifications are globally recognized, opening doors across international markets.
Why Master Professional Accounting Outperforms Bachelor DegreesUnlike traditional bachelor programs that cover broad business concepts, the Master of Professional Accounting is laser-focused on professional competencies. This specialized approach means graduates enter the workforce with immediately applicable skills rather than theoretical knowledge that requires years of practical experience to become valuable.
The program structure typically covers advanced financial reporting, auditing principles, taxation law, management accounting, and corporate governance. These subjects directly align with CPA Australia's educational requirements, eliminating the need for additional bridging courses that bachelor graduates often face. Students save both time and money while gaining deeper expertise in critical areas.
Most importantly, the Master of Professional Accounting functions as a conversion degree, welcoming students from diverse academic backgrounds. Whether you studied engineering, arts, or science, this program transforms your existing knowledge into accounting expertise. This diversity actually strengthens graduates' problem-solving abilities, as they bring unique perspectives to traditional accounting challenges.
The CPA Fast Track AdvantageAchieving CPA status traditionally requires completing specific educational requirements, gaining relevant work experience, and passing professional examinations. The Master of Professional Accounting accelerates this timeline significantly by satisfying all educational prerequisites in a condensed timeframe.
Professional accounting bodies including CPA Australia, Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand (CA ANZ), and the Institute of Public Accountants (IPA) have accredited quality programs to ensure graduates meet industry standards. This accreditation means employers immediately recognize the qualification's value, often leading to higher starting salaries and faster career advancement.
The program's practical focus also provides networking opportunities that prove invaluable for career development. Many institutions maintain strong industry connections, facilitating internships, guest lectures from senior practitioners, and recruitment events where students connect directly with potential employers.
Career Pathways Beyond Traditional AccountingModern accounting professionals operate far beyond basic bookkeeping and tax preparation. Today's CPAs function as strategic business advisors, helping organizations navigate complex financial decisions, regulatory compliance, and performance optimization. The Master of Professional Accounting prepares graduates for these evolved responsibilities.
Corporate accounting roles now encompass business intelligence, financial planning and analysis, risk management, and sustainability reporting. Government positions offer stability while contributing to public sector financial management and policy development. Public practice provides variety, working with diverse clients from small businesses to multinational corporations.
Emerging areas like forensic accounting, environmental accounting, and blockchain auditing represent exciting opportunities for tech-savvy graduates. These specialized fields often command premium salaries while offering intellectually stimulating career paths that didn't exist even five years ago.
Choosing the Right InstitutionNot all Master of Professional Accounting programs deliver equal value. When evaluating options, prioritize institutions with strong industry connections, experienced faculty, and comprehensive student support services. NAPS offers a Bachelor of Business (Accounting) that provides excellent foundational knowledge before advancing to master's level studies.
Look for programs that emphasize practical application through case studies, internships, and real-world projects. The best institutions also provide career counseling, resume workshops, and interview preparation to ensure graduates successfully transition into professional roles.
Accreditation by relevant professional bodies remains non-negotiable. This recognition ensures your qualification meets industry standards and facilitates professional membership applications. Additionally, consider the institution's reputation among employers, as prestigious alumni networks often provide career advantages that extend well beyond graduation.
The Master of Professional Accounting represents more than an educational qualification – it's a strategic career investment that delivers both immediate opportunities and long-term professional growth. For motivated individuals seeking the fastest route to CPA certification and accounting success, this specialized program provides unmatched value in today's competitive market.
Transform your career potential today – contact NAPS to learn how our accredited accounting programs can unlock your CPA pathway.

Islamic Business vs Traditional: Australia Career Boom
Australia's business landscape is experiencing a remarkable transformation as Islamic business principles gain mainstream recognition and adoption. The growing halal economy, valued at over $2.3 trillion globally, presents unprecedented career opportunities for graduates who understand both Islamic and conventional business frameworks.
This shift reflects Australia's increasingly diverse population and economy, where multicultural competency has become a valuable professional asset. Forward-thinking organizations recognize that Islamic business principles – emphasizing ethical conduct, social responsibility, and sustainable practices – align perfectly with modern corporate values and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) priorities.
Understanding Islamic Business PrinciplesIslamic business operates on fundamental principles that differ significantly from purely profit-driven traditional models. The concept of halal (permissible) extends beyond food products to encompass ethical business practices, fair trading, and socially responsible investment strategies.
Key principles include prohibition of riba (excessive interest), gharar (excessive uncertainty), and gambling-related activities. Instead, Islamic business emphasizes profit-sharing, asset-backed financing, and risk-sharing partnerships. These principles create more stable, community-focused business models that have proven remarkably resilient during economic downturns.
The concept of maslaha (public interest) drives Islamic businesses to consider broader social impacts beyond shareholder returns. This holistic approach resonates with younger consumers and employees who increasingly prioritize purpose-driven organizations over purely profit-maximizing entities.
Traditional Business Model LimitationsConventional business education often focuses narrowly on profit maximization, shareholder primacy, and competitive advantage. While these concepts remain important, they represent incomplete approaches to modern business challenges.
Traditional models frequently struggle with sustainability concerns, social inequality, and long-term stakeholder relationships. The 2008 financial crisis and subsequent economic challenges highlighted the risks of purely profit-driven decision-making without considering broader consequences
Many traditional businesses now actively seek professionals who understand alternative business frameworks that can complement conventional approaches. This demand creates significant opportunities for graduates with Islamic business knowledge to provide fresh perspectives and innovative solutions.
Career Opportunities in Australia's Halal EconomyAustralia's halal economy encompasses far more than food certification and restaurant management. The sector includes halal tourism, Islamic finance, modest fashion, halal pharmaceuticals, and ethical investment products. Each area offers distinct career pathways for qualified professionals.
Islamic finance represents one of the fastest-growing segments, with major Australian banks now offering Shariah-compliant products. Career opportunities include Islamic banking specialists, Shariah compliance officers, and ethical investment advisors. These roles typically command premium salaries due to specialized knowledge requirements.
The halal tourism sector capitalizes on Australia's appeal to Muslim travelers worldwide. Career opportunities span hotel management, tour operations, destination marketing, and cultural consulting. As Muslim populations grow globally, this sector's expansion potential remains enormous.
Competitive Advantages for Islamic Business GraduatesProfessionals with Islamic business education possess unique competitive advantages in today's market. They understand both conventional and alternative business frameworks, enabling them to serve diverse client bases and navigate complex multicultural business environments.
This dual competency proves particularly valuable in international business, where cultural sensitivity and ethical considerations increasingly influence success. Organizations expanding into Muslim-majority markets specifically seek professionals who understand local business customs and religious considerations.
The growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility and sustainable business practices aligns naturally with Islamic business principles. Graduates can articulate how traditional Islamic concepts apply to modern challenges like climate change, social inequality, and ethical governance.
Educational Pathways and Career DevelopmentNAPS offers a Bachelor of Islamic Business that provides comprehensive grounding in both Islamic and conventional business principles. This unique program prepares graduates for diverse career opportunities while maintaining cultural authenticity and religious integrity.
The curriculum typically covers Islamic commercial law, halal industry management, ethical finance, and cross-cultural business communication. Students also study conventional subjects like marketing, accounting, and operations management, ensuring broad professional competency.
Practical experience through internships with halal-certified businesses, Islamic financial institutions, and multicultural organizations provides real-world application of theoretical knowledge. These experiences often lead directly to employment opportunities as organizations recognize graduates' unique value propositions.
Future Growth ProjectionsIndustry analysts project continued expansion of Australia's halal economy, driven by demographic changes, increased consumer awareness, and growing acceptance of ethical business practices. This growth translates directly into career opportunities for qualified professionals.
The integration of Islamic business principles into mainstream corporate governance represents another significant trend. As organizations seek sustainable, ethical business models, professionals who understand these principles become increasingly valuable strategic assets.
Government initiatives supporting multicultural business development and international trade with Muslim-majority countries further enhance career prospects. These policies create supportive environments for Islamic business professionals to thrive and contribute to Australia's economic growth.
The choice between Islamic business and traditional business education isn't binary – the most successful professionals understand both frameworks and can apply appropriate principles to specific situations. This comprehensive knowledge positions graduates for leadership roles in Australia's evolving, multicultural business environment.
Bridge traditional and Islamic business expertise – contact NAPS today to discover how our specialized programs prepare you for multicultural career success.

Master in Professional Accounting in Australia – Your Pathway to a Global Career
Thinking about a high-impact career that opens doors not just locally but globally? The world of accounting offers stability, growth, and endless opportunities, and pursuing a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia could be your golden ticket. It’s a qualification designed to transform your career, whether you’re starting fresh or looking to gain the credentials you need to level up. But we know the path can seem complex, filled with questions about courses, careers, and requirements.
This guide is here to help you navigate it all with confidence. We’ll break down everything you need to know, from why Australia is the perfect place for your studies to the exact steps you can take to get started.
- First, we’ll explore why Australia is a top global destination for accounting education.
- Next, we will demystify the Master of Professional Accounting (MPA) degree itself.
- Then, you will discover the exciting and lucrative career paths this degree unlocks.
- After that, we'll guide you on how to choose the right program for your goals.
- Finally, we will provide a clear checklist to help you apply and succeed in your studies.
Why Choose Australia for Your Professional Accounting Master's?
Deciding where to invest in your education is a huge step, and it’s important to understand the benefits of your chosen destination. When you choose to study accounting in Australia, you’re not just signing up for a course; you’re stepping into a vibrant ecosystem built for your success. The country’s reputation for high-quality education is backed by a strong, growing economy that actively seeks skilled accounting professionals.
This combination of world-class learning and real-world demand makes Australia a strategic choice for anyone serious about building a successful accounting career. From gaining qualifications that are respected worldwide to enjoying an unmatched quality of life, the advantages are clear. Let’s explore exactly what makes Australia stand out on the world stage.
A Globally Recognised Qualification
One of the most significant advantages of completing a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia is the global recognition that comes with it. Australian universities and higher education providers are held to incredibly high standards under the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF). This ensures that your degree is not just a piece of paper but a symbol of excellence respected by employers and professional bodies worldwide.
This global stamp of approval means your career opportunities aren't limited to Australia's borders. Whether you dream of working in London, Singapore, Toronto, or back in your home country, your Australian MPA will be a powerful asset. It signals that you have received a rigorous, modern, and comprehensive education in accounting principles and practices.
Strong Economic Growth and High Demand for Accountants
Australia’s economy is resilient and consistently growing, which directly fuels the demand for qualified accountants. According to the Australian Government's Job Outlook data, the number of Accountants is expected to grow strongly over the next five years. This creates a stable and promising job market for MPA graduates.
Businesses of all sizes, from innovative tech startups to multinational corporations and government agencies, rely on skilled accountants for financial management, strategic planning, and regulatory compliance. This constant need means that graduates with a professional accounting masters in Australia are highly sought after. You are entering a field where your skills are not just valued but essential for economic progress.
A Clear Pathway to Professional Accreditation
For many aspiring accountants, the ultimate goal is to become a Certified Practising Accountant (CPA) or a Chartered Accountant (CA). An accredited Master of Professional Accounting is the most direct pathway to achieving these prestigious credentials. Programs like the one offered at NAPS are designed to meet the educational requirements of CPA Australia, Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand (CA ANZ), and the Institute of Public Accountants (IPA).
This alignment is a game-changer because it streamlines your journey to becoming professionally certified. Instead of taking disparate bridging courses, your master’s degree covers the necessary foundational knowledge in areas like auditing, taxation, and financial reporting. This integrated approach saves you time, money, and effort on your path to full professional status.
What is a Master of Professional Accounting (MPA)? A Deep Dive
Now that you know why Australia is the place to be, let's look closer at the degree itself. The Master of Professional Accounting (MPA) is a specialised postgraduate program, and understanding its structure is key. Unlike general business degrees, professional accounting courses Australia are purpose-built to equip students with the specific technical skills and theoretical knowledge required for a career in accounting.
The MPA is often designed as a conversion degree, making it perfect for individuals from non-accounting backgrounds who want to pivot their careers. It’s an intensive, focused program that gets you job-ready in a relatively short amount of time. Let’s break down who it’s for and what you’ll learn.
Who is the MPA Designed For?
You might be surprised to learn that you don't necessarily need an undergraduate degree in accounting to enrol in an MPA. This is one of its greatest strengths! The MPA is ideal for two main groups of people:
- Career Changers: Individuals who hold a bachelor's degree in another field (like arts, science, engineering, or IT) and want to move into the stable and rewarding field of accounting.
- International Graduates: Students whose undergraduate accounting degrees from their home country are not recognised by Australian professional bodies and need a qualifying degree to pursue accreditation.
Essentially, if you have the ambition to become an accountant but lack the formal educational prerequisites, the MPA is your bridge to that goal. It provides all the foundational and advanced knowledge in one comprehensive package.
Core Subjects You'll Master
The curriculum of a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia is carefully structured to cover all the essential pillars of the profession. At NAPS, for example, the course ensures you develop a deep understanding of key areas that are critical for professional practice and accreditation. You can expect to dive into subjects such as:
- Financial Accounting: Learning how to prepare and interpret financial statements for companies.
- Management Accounting: Using financial data to make strategic business decisions.
- Auditing and Assurance: Understanding the process of verifying financial records for accuracy and compliance.
- Australian Taxation Law: Navigating the complexities of personal and corporate tax.
- Corporate Law: Grasping the legal frameworks that govern business operations.
- Data Analytics & AI in Accounting: Adopting modern technologies to analyze financial data for better business insights.
These subjects don't just teach you theory; they prepare you for the real-world challenges you’ll face as a professional accountant.
Unlocking Your Career: Job Opportunities After Graduation
Completing your MPA is just the beginning of an exciting journey. The skills you gain are universally applicable, making you a valuable asset in virtually every industry. An accounting career in Australia is not just about crunching numbers in a quiet office; it's about becoming a trusted advisor who helps organisations thrive in a complex financial landscape.
Your qualification opens doors to a wide variety of roles, each with its own unique challenges and rewards. From ensuring public companies are transparent to helping non-profits manage their funds effectively, your work will have a real impact. Here are some of the paths you can take.
In-Demand Roles for MPA Graduates
With a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia, you will be qualified for a range of specialised roles. You're not limited to one single job title. Here are just a few of the career paths that will be open to you:
- Financial Accountant: Responsible for maintaining financial records and preparing reports for external stakeholders like investors and regulators.
- Management Accountant: Works internally to provide financial information that helps managers make strategic decisions.
- Auditor: Can work for an accounting firm (external) or within a company (internal) to examine financial records for accuracy and compliance.
- Tax Accountant/Consultant: Specialises in tax law, helping individuals and businesses comply with regulations and minimise their tax liability.
- Forensic Accountant: Investigates financial discrepancies and fraud, often working with law enforcement agencies.
- Business Advisor: Uses financial expertise to provide strategic advice to businesses on growth, efficiency, and risk management.
Salary Expectations: What Can You Earn?
Of course, financial reward is an important factor when considering a new career. The good news is that accounting is a well-compensated profession in Australia, with strong potential for salary growth as you gain experience and professional certification.
While starting salaries can vary by location and company size, graduates with a master's degree can expect a competitive entry-level package. According to data from platforms like Seek and Payscale, graduate accountants in Australia can earn between $65,000 and $80,000 per year. With a few years of experience and a CPA or CA designation, this can quickly rise to over $100,000 and continue to grow from there.
Choosing the Right Program: What to Look for in an MPA
Not all MPA programs are created equal, and choosing the right one is crucial for your success. The ideal course should not only provide you with the necessary knowledge but also support you throughout your learning journey. When evaluating your options, consider factors beyond the curriculum, such as accreditation, flexibility, and the institution’s focus on practical success, which is where the NAPS accounting course truly shines.
Making an informed decision means looking for a provider that is genuinely invested in your future. You want a program that bridges the gap between the classroom and the workplace. Here are the key things to look for.
Accreditation and Industry Recognition
This is non-negotiable. Ensure the MPA program you choose is fully accredited by Australia’s key professional accounting bodies: CPA Australia and Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand (CA ANZ). This accreditation is your guarantee that the course content meets the high standards required for you to pursue professional certification after you graduate.
A program like the Master of Professional Accounting at NAPS is specifically designed with these accreditation requirements in mind. This saves you the headache of figuring out if you’ve met the prerequisites later on. It provides a seamless and clear pathway toward your professional goals.
The NAPS Advantage: A Focus on Real-World Success
Beyond just teaching theory, a great MPA program prepares you for the realities of the modern workplace. At NAPS, the focus is on creating job-ready graduates who can make an immediate impact. The curriculum for the Master in Professional Accounting in Australia is infused with real-world case studies and practical applications to ensure you can apply what you learn.
This approach means you're not just memorising formulas; you're learning how to solve real business problems. With experienced lecturers who bring their industry knowledge into the classroom, you gain insights that go beyond the textbook. This practical focus is what employers are looking for and what will set you apart in the job market.
Your Application Checklist: Steps to Enrol and Succeed
Feeling ready to take the next step? The application process can seem daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes it much easier. To secure your place in a program, you’ll need to meet the entry requirements for master of accounting and prepare a thorough application. This checklist will guide you through the key stages.
Remember, preparation is key to a smooth and successful application. Start gathering your documents early and don’t hesitate to reach out to the institution’s admissions team if you have any questions. They are there to help you succeed.
Understanding the Entry Requirements
First, confirm that you meet the basic eligibility criteria. While this can vary slightly between institutions, the typical requirements for a Master of Professional Accounting in Australia include:
- A completed bachelor's degree from a recognised university in any discipline.
- Proof of English language proficiency for non-native speakers, usually through a test like IELTS or TOEFL.
- Some institutions may have a minimum Grade Point Average (GPA) requirement from your previous studies.
The NAPS admissions team can provide clear guidance on their specific entry requirements and help you assess your eligibility.
Preparing Your Application Documents
Once you’ve confirmed your eligibility, it’s time to gather your paperwork. A typical application package for a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia will require:
- Certified copies of your academic transcripts and degree certificate.
- Your English language test results (e.g., IELTS).
- A copy of your passport.
- A current curriculum vitae (CV) or resume.
- A personal statement or letter of intent, explaining why you want to pursue the degree.
Having these documents ready will make the online application process much smoother and faster.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Do I need a background in business or accounting to apply for an MPA?
No, you don’t! The Master of Professional Accounting is specifically designed as a conversion course. It’s perfect for graduates from any discipline—be it arts, sciences, or engineering—who want to pivot into an accounting career.
- Is a Master in Professional Accounting from Australia recognised internationally?
Absolutely. Australian qualifications are highly respected globally, and degrees accredited by CPA Australia and CA ANZ are recognised by professional bodies around the world. This gives you excellent career mobility.
- How long does it take to complete the degree?
Most Master of Professional Accounting programs in Australia, including the one at NAPS, are designed to be completed over 2 years of full-time study. This timeframe allows you to cover all the required knowledge for professional accreditation.
- What is the difference between an MPA and a Master of Finance?
An MPA focuses broadly on accounting principles, including financial reporting, auditing, taxation, and management accounting, preparing you to become a CPA or CA. A Master of Finance is more specialised, focusing on investments, financial markets, and corporate finance, leading to roles like financial analyst or investment banker.
- Can I work in Australia after completing my MPA?
Yes, many international students are eligible to apply for a Temporary Graduate visa (subclass 485) after completing their studies. This visa allows you to live, study, and work in Australia for a temporary period, giving you the chance to gain valuable local work experience.
- What are the typical fees for a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia?
Fees can vary between institutions. It's best to check the official website of the provider you're interested in, like the NAPS course page, for the most current and accurate fee information for both domestic and international students.
Conclusion: Your Future in Accounting Starts Today
Embarking on a Master in Professional Accounting in Australia is more than just an academic decision—it's an investment in a secure, rewarding, and globally mobile future. From gaining a world-class qualification to unlocking a direct pathway to professional accreditation and high-demand careers, the benefits are undeniable. We hope this guide has demystified the process and empowered you with the clarity and confidence to move forward.
The journey may seem long, but every successful career starts with a single, decisive step. You have the ambition, and with the right program and support, you can achieve your professional goals. The world of accounting is waiting for sharp, dedicated minds like yours.
Ready to take that first step? Our friendly team is here to answer your questions and guide you through the process.
Explore more with NAPS and get started on your pathway to success: https://www.naps.edu.au/contact-us

Bachelor of Islamic Business: Career & Faith Guide
Have you ever felt caught between building a successful career and staying true to your personal values? You’re not alone.
Many aspiring professionals today are searching for a path that offers both financial stability and spiritual fulfillment, and that's where a unique and powerful degree comes into the picture.
This guide is your friendly introduction to the Bachelor of Islamic Business program, a qualification designed for the modern world.
We'll walk through what it is, what you’ll learn, and where it can take you, all in a simple and encouraging way.
Think of this as a conversation with a friend who has done the research and wants to help you see the incredible opportunities ahead.
We understand that choosing a degree is a huge decision, and it can feel a bit overwhelming with all the options out there.
But by the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how this program bridges the gap between traditional business education and faith-based principles. Let's explore how you can build a meaningful career without compromising what matters most to you.
What Exactly is a Bachelor of Islamic Business?
At its heart, a Bachelor of Islamic Business program is a university-level degree that teaches you the fundamentals of commerce, management, and finance through the lens of Islamic principles.
It’s designed to create ethical leaders who can navigate the global economy with a strong moral compass. It’s about building profitable, sustainable businesses that also contribute positively to society.
Beyond the Name: A Modern Approach to Ethical Commerce
Don't let the name mislead you into thinking this degree is only about theology; it is a robust and practical business qualification. Think of it as a standard business degree with an added layer of ethical guidance drawn from Shariah principles, which emphasize fairness, transparency, and social responsibility. This ethical framework isn't just a footnote—it's woven into every subject you study.
The goal is to equip you with all the essential business skills you need to succeed while ensuring your actions are principled and just.
This approach is gaining incredible traction worldwide as more consumers and investors look for businesses that do more than just make a profit. You’ll learn how to build enterprises that are both successful and a source of good in the world.
This unique combination makes graduates highly valuable in a world that is increasingly focused on ethical and sustainable practices.
A Bachelor of Islamic Business program prepares you not just for a job, but for a purpose-driven career. It empowers you to become a leader who understands that true success is measured by more than just the bottom line.
The Core Difference: How It Compares to a Traditional BBA
So, what makes a Bachelor of Islamic Business program different from a conventional Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA)? While both degrees cover core topics like marketing, accounting, and management, the foundational philosophy is what sets them apart. A traditional BBA is typically based on secular, capitalist principles focused on maximizing shareholder wealth.
In contrast, an Islamic business degree is built upon the principles of Shariah, which prioritizes justice, risk-sharing, and the well-being of all stakeholders, including customers, employees, and the community.
For example, instead of learning about interest-based loans (Riba), you will study profit-sharing models like Mudarabah and Musharakah. The focus shifts from pure profit maximization to creating shared value.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the key philosophical differences:
- Objective: Traditional BBA often focuses on shareholder profit, while an Islamic business degree emphasizes community welfare and ethical returns.
- Financial Instruments: You'll learn about Shariah-compliant financing (like Sukuk bonds) instead of conventional, interest-bearing instruments.
- Risk: Islamic finance promotes sharing risk between the lender and the borrower, whereas conventional finance often transfers risk entirely to the borrower.
Is This Program Right for You?
Wondering if this degree aligns with your aspirations? If you find yourself nodding along to the following points, a Bachelor of Islamic Business program could be the perfect fit for you. It's a path for those who want to make a real difference in the world of commerce.
You might be an ideal candidate if you:
- Believe that business should have a positive impact on society.
- Want a career that aligns with your personal faith and ethical values.
- Are interested in the rapidly growing global market for Halal products and services.
- See yourself as an entrepreneur who wants to build a business on a foundation of fairness.
- Are fascinated by the idea of ethical finance and investment that avoids speculation and uncertainty.
If these ideas resonate with you, you're in the right place. This degree is less about what you want to do and more about who you want to be as a business professional. It’s about leading with integrity in every decision you make.
What You'll Learn: A Peek Inside the Curriculum
One of the best things about a Bachelor of Islamic Business program is that it provides a comprehensive education, giving you the best of both worlds.
You will graduate with a solid understanding of contemporary business practices, enriched with the wisdom of Islamic commercial law. This dual-focus curriculum is what makes the degree so powerful and relevant.
The Foundational Pillars: Core Business Subjects
First and foremost, you will build a rock-solid foundation in all the essential areas of business management and administration.
These are the universal skills that every successful business leader needs, regardless of their industry. You can expect to master the same core subjects found in any top-tier business school.
These foundational courses typically include:
- Principles of Management: Learning how to lead teams, manage projects, and organize resources effectively.
- Marketing Fundamentals: Understanding how to connect with customers and build a strong brand identity.
- Financial Accounting: Mastering the language of business to track, report, and analyze financial health.
- Business Law and Ethics: Studying the legal frameworks that govern commerce, with a special focus on ethical conduct.
- Human Resource Management: Learning how to recruit, train, and motivate a productive and happy workforce.
The Islamic Specialization: Where Faith Meets Finance
This is where the program truly shines and sets itself apart from any other business degree you might consider. Alongside the core subjects, you will dive deep into specialized courses that explore business and finance from an Islamic perspective. These subjects provide the ethical framework that will guide your entire career.
You’ll explore fascinating topics such as:
- Islamic Economics: Understanding an economic system based on social justice and equitable distribution of wealth.
- Islamic Banking and Finance: Studying the principles and practices of interest-free banking and Shariah-compliant investments.
- Takaful (Islamic Insurance): Learning about cooperative insurance models based on mutual support and shared responsibility.
- Halal Supply Chain Management: Mastering the logistics of ensuring products and services are compliant from source to consumer.
- Zakat and Waqf Management: Understanding the institutions of Islamic charity and endowments and their role in social development.
Developing Practical Skills for the Real World
Theoretical knowledge is important, but applying it is what truly matters. Reputable institutions, like the National Aacdemy of Professional Studies (NAPS), emphasize hands-on learning that prepares you for the challenges of the modern workplace. A good Bachelor of Islamic Business program will be packed with practical application.
You’ll engage in case studies of real-world Islamic businesses, participate in group projects that simulate launching a Shariah-compliant startup, and may even have internship opportunities with Islamic banks or ethical investment firms.
This focus on practical skills ensures you don't just graduate with a degree, but with the confidence and competence to excel from day one. The goal is to make you job-ready for a global market that desperately needs your unique skills.
Unlocking Your Future: Career Paths After Graduation
Graduating with a Bachelor of Islamic Business program opens doors to a diverse and rapidly expanding range of career opportunities. The global Islamic economy is valued in the trillions of dollars and is growing every year, creating immense demand for qualified professionals. You will be uniquely positioned to thrive in this dynamic sector.
Thriving in the World of Islamic Finance
The most direct career path for graduates is within the burgeoning Islamic finance industry. This sector includes banking, asset management, and insurance, all operating under Shariah principles. You’ll be qualified for roles that are not only financially rewarding but also ethically sound.
Here are some of the exciting job roles you could pursue:
- Islamic Banker: Working in retail or corporate banking, offering Shariah-compliant products like Murabaha (cost-plus financing) or Ijarah (leasing).
- Shariah Advisor or Auditor: Ensuring a financial institution's products and operations comply with Islamic law.
- Takaful Specialist: Developing and managing ethical insurance products based on mutual cooperation.
- Islamic Fund Manager: Managing investment portfolios that screen for ethical and Halal-compliant securities.
Beyond Finance: Diverse Opportunities in Business
The skills you gain are not limited to the finance sector; they are transferable across a huge range of industries. The principles of ethical conduct, fairness, and social responsibility are valuable everywhere. A Bachelor of Islamic Business program makes you a versatile candidate for many different roles.
Consider these diverse career paths:
- Halal Industry Consultant: Helping businesses in food, tourism, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals achieve Halal certification.
- Ethical Marketing Manager: Crafting marketing campaigns that are truthful, transparent, and respectful of consumer values.
- Socially Responsible Entrepreneur: Launching your own business with a mission to solve a community problem or promote ethical practices.
- Non-Profit Manager: Leading charitable organizations, especially those focused on Zakat collection and distribution or managing Awqaf (endowments).
A Real-World Example
Imagine a graduate named Fatima who completed her Bachelor of Islamic Business program. She was passionate about both technology and community development. Instead of taking a traditional finance job, she launched a fintech startup that developed an app to help small businesses access Shariah-compliant micro-financing.
Her company not only became profitable but also empowered hundreds of local entrepreneurs to grow their businesses without resorting to interest-based debt. Fatima's story shows how this degree provides the tools to innovate and create solutions that are both commercially viable and socially beneficial. It’s a testament to how you can truly blend your passion with your principles.
Choosing the Right Institution: What to Look For
Selecting where you study is just as important as deciding what you study. The right institution will not only provide you with a quality education but also support you on your journey. When researching where to enroll in a Bachelor of Islamic Business program, there are a few key factors to consider.
Accreditation and Recognition
First and foremost, ensure the program and the institution are fully accredited by the relevant educational authorities, like Australia's Tertiary Education Quality and Standards Agency (TEQSA).
Accreditation is your guarantee that the degree meets rigorous academic standards and will be recognized by employers globally. A recognized degree from an institution known for quality, such as NAPS, adds significant weight to your resume.
Faculty Expertise and Industry Connections
Look for a university or institute where the faculty members are not just academics but also have real-world experience in Islamic business and finance. Instructors who have worked as Shariah advisors, bankers, or entrepreneurs can provide invaluable insights that you won't find in a textbook. Strong industry connections also lead to better internship opportunities and networking events, giving you a head start in your career.
A Supportive and Inclusive Learning Environment
Your educational journey should be an enriching and supportive one. Choose an institution that values student well-being and fosters a strong sense of community.
Look for student support services, career counseling, and an environment that is welcoming to students from all backgrounds who are interested in ethical business, like the student-centric approach often found at NAPS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Do I need to be Muslim to enroll in a Bachelor of Islamic Business program?
Absolutely not. This program is open to students of all faiths and backgrounds who are interested in ethical business, social responsibility, and alternative economic systems. The principles of fairness, transparency, and community welfare are universal values that appeal to anyone wanting to make a positive impact through commerce. - What are the typical entry requirements for this program?
Entry requirements are similar to most bachelor's degrees and typically include the successful completion of secondary education (like an Australian Year 12 certificate or its international equivalent). Some institutions may have specific prerequisites in subjects like English or mathematics, so it's always best to check directly with the admissions office of the institution you're interested in. - Is a Bachelor of Islamic Business respected internationally?
Yes, it is highly respected, especially given the multi-trillion dollar growth of the global Islamic economy. Graduates are sought after in the Middle East, Southeast Asia (like Malaysia and Indonesia), Europe, and North America. The ethical and financial skills you learn are globally transferable and in high demand. - Can I pursue a Master's or MBA after completing this degree?
Of course. A Bachelor of Islamic Business program provides a strong foundation that allows you to pursue a wide range of postgraduate studies, including a traditional MBA, a specialized Master's in Islamic Finance, or a PhD. It fully prepares you for advanced academic work in business and finance. - How much math is involved in the finance courses?
The finance courses will involve quantitative analysis, but they are designed to be accessible. You will learn the necessary mathematics within the context of the subjects, focusing on practical application rather than abstract theory. If you can handle high-school level math and are willing to learn, you will be well-equipped to succeed. - What is the main difference between "Islamic finance" and "ethical finance"?
This is a great question! "Ethical finance" is a broad term for investments that consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Islamic finance is a specific type of ethical finance that is guided by the principles of Shariah, which includes all the ESG considerations plus additional rules, such as the prohibition of interest (Riba) and investment in certain industries (like alcohol or gambling).
Your Path to a Purpose-Driven Career Starts Here
Choosing a degree is more than just planning for a job; it's about shaping your future and deciding the kind of impact you want to have on the world. A Bachelor of Islamic Business program offers a unique and powerful opportunity to build a successful career that is deeply aligned with your values of integrity, fairness, and community.
You don't have to separate your professional ambitions from your personal principles—this degree proves you can have both.
You've taken the first step by learning about what this incredible field has to offer. You now know that it provides a robust, practical business education with an ethical foundation that is more relevant today than ever before.
You are ready to become a National kind of leader—one who measures success not just in profit, but in purpose.
Your journey forward is an exciting one. The next step is to explore the specific business programs offered by leading institutions that value practical skills and student success.
Exploring the courses at a provider like the National Academy of Professional Studies (NAPS) could be a fantastic way to see how you can turn this knowledge into a real-world career.

My Strategic Journey as an Accounting Student
When “accounting” is discussed, it is usually thought of as numbers, calculations and boring spreadsheets. I was not any different either. But now, as an accounting student, having amassed a lot of knowledge, I have realized that it is much more than that. It is more about understanding how money works, how businesses survive and grow and how important it is to keep things fair and honest. Accounting is just that.
Why I Chose Accounting?
I chose accounting because I wanted to do something practical and useful. Every business need someone to manage its money properly. That means no matter where I work big company or small shop, accounting will always be important.
Also, I enjoy organizing things and solving problems, and accounting gives me that chance. There is a certain satisfaction when your numbers match, or when you figure out where something went wrong and fix it.
What I’ve Learned So Far?
My academic experience has enabled me with the ability to prepare and interpret key financial documents such as balance sheets, income statements and cash flow statements. I have developed and improved technical ability in recording transactions, analysing financial health and finding risk.
On an equally important note, I have also adapted essential soft skills like time management, team collaboration and the ability to communicate complex financial concepts in accessible terms. Accounting has taught me that trust and ethical responsibility are foundational. A minor miscalculation or lapse in integrity can compromise not just financial statements but entire organisations.
The Struggles Are Real
Studying accounting has its challenges. Mastering complex standards, reconciling financial differences and meeting academic deadlines can be overwhelming. There are times when the pressure to support accuracy and consistency feels relentless. However, every challenge has reinforced my analytical mindset, attention to detail and persistence traits which are essential for both professional success and personal growth.
My Hopes for the Future
In the future, I want to become a professional accountant, even get my CPA or CA license. I want to help businesses make smart decisions and stay financially healthy. Most of all, I want to do a job that makes a difference.
Final Thoughts
If you are thinking about studying accounting, just know this it is not easy, but it is worth it. It teaches you responsibility, patience, and problem-solving. And once you get into it, you will see that it is actually interesting.
Being an accounting student has helped me grow not just academically, but as a person. I am proud to be on this journey, even on the days when the calculator and I do not get along!

Rising Demand, Real Impact: Why the Bachelor of Social Work is the Future of Care and Community
As Australia faces growing challenges in mental health, aged care, family services, and community wellbeing, social work is emerging as a vital profession for the country’s future. The Bachelor of Social Work is more than a degree—it’s a pathway to a meaningful, stable, and in-demand career.
National Trend: A Growing Need for Social Workers
The Australian Government’s Labour Market Insights report highlights that the demand for qualified social workers is expected to grow strongly in the coming years. Between 2023 and 2028, social work jobs are projected to grow by over 23 percent.
This increase is driven by:
- Greater focus on mental health services
- Expanding aged care and disability support
- Government investment in child protection and family services
- The need for culturally competent professionals in ever increasing multi-cultural communities
Why International Students Should Consider Social Work
Social work is recognised as a skill shortage area in several Australian states, which opens doors to potential migration opportunities through state nomination and skilled visa programs.
Other benefits include:
- Qualifications that are nationally accredited and recognised (often through AASW – Australian Association of Social Workers)
- Diverse employment opportunities in government agencies, non-profits, healthcare, education, community organisations and pathways for research careers
- Opportunities to build strong professional skills in communication, cultural sensitivity, and case management
- A career that provides emotional rewards alongside professional growth
Career Opportunities After Graduation
Graduates with a Bachelor of Social Work may pursue roles such as:
- Mental health social worker
- Child and family support officer
- Community development worker
- Hospital or school social worker
- Aged care or disability services coordinator
- Crisis intervention or domestic violence case manager
Many of these roles appear on Australia’s skilled occupation lists, offering a clear path for international graduates who wish to stay and work in the country.
Why Social Work Matters
Social work combines professional knowledge with a deep sense of empathy and service. It is a career for those who want to make a lasting impact—whether by supporting individuals through hardship, strengthening families, or advocating for vulnerable communities.
If compassion is in your DNA, the world needs you now more than ever.
The challenges around us are many — injustice, inequality, suffering — but what we need are people bold enough to face them head-on. People with heart. People with courage.
At NAPS, we don’t just train social workers — we shape change-makers.
We’ll equip you with the skills to think critically, act creatively, and respond with innovation in the face of real-world problems.
‘Let's get this right, when compassion meets action, everything changes'
24/04/2025 Professor Venkat Pulla
Choosing to study a Bachelor of Social Work is both a smart and compassionate decision. It leads to a career with strong job prospects, personal fulfilment, and the potential to contribute meaningfully to Australian society. For international students, it also offers long-term opportunities and a chance to be part of a profession that changes lives.

IFRS in Australia: A Guide to Financial Transparency and Accountability
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) form the backbone of financial reporting in Australia. Since their adoption in 2005, IFRS has shaped how businesses communicate financial information, ensuring consistency and transparency. But what does this mean in practical terms for businesses, investors, and the broader economy?
The Role of IFRS in Financial Reporting
IFRS is a set of internationally accepted accounting standards issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). Its primary goal is to create a common financial language that facilitates comparability and reliability across global markets. Over 140 countries, including Australia, have adopted IFRS, making it a fundamental element of financial regulation and reporting.
In Australia, the Australian Accounting Standards Board (AASB) is responsible for implementing IFRS while considering local economic and regulatory factors. This ensures that financial statements meet global expectations while addressing specific national requirements.
Why IFRS Matters to Australian Businesses
For companies operating in Australia, IFRS compliance is not just a regulatory obligation but a strategic advantage. Standardised financial statements help investors, creditors, and stakeholders make informed decisions, reducing uncertainty and enhancing market confidence.
Before IFRS, different national accounting standards created inconsistencies that made financial comparisons difficult. Now, whether an investor is assessing an Australian firm or a European counterpart, IFRS ensures that financial data is presented in a uniform and understandable manner.
Key IFRS Standards Impacting Australian Businesses
Several IFRS standards significantly impact how companies report financial information in Australia:
- Revenue Recognition (AASB 15/IFRS 15): Establishes clear guidelines on when and how businesses recognise revenue, reducing discrepancies and enhancing consistency.
- Lease Accounting (AASB 16/IFRS 16): Requires companies to record most lease obligations on their balance sheets, offering a more accurate picture of liabilities.
- Financial Instruments (AASB 9/IFRS 9): Regulates how businesses classify and measure financial assets and liabilities, improving transparency in risk assessment.
How IFRS Affects Investors and Everyday Australians
IFRS extends beyond businesses and accountants—it influences anyone with an interest in financial markets. Investors, for instance, rely on IFRS-based reports to assess company performance and make informed decisions. Superannuation funds, which manage retirement savings for millions of Australians, also depend on IFRS-compliant financial statements to evaluate asset performance and risk exposure.
Moreover, IFRS supports economic stability by promoting confidence in financial reporting. When businesses adhere to a globally recognised standard, stakeholders can trust the accuracy of financial information, reducing the likelihood of financial misstatements and corporate scandals.
The Future of IFRS in Australia
Financial reporting standards continue to evolve, reflecting changes in business models, digital transformation, and sustainability concerns. The AASB actively monitors and updates IFRS standards to ensure they remain relevant to Australian businesses and investors.
One emerging area of interest is sustainability accounting, which integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into financial reporting. As global markets place greater emphasis on sustainability, new IFRS standards are being developed to provide consistent reporting frameworks for ESG disclosures.
Final Thoughts
IFRS plays an essential role in maintaining transparency, accountability, and trust in Australia’s financial system. Whether you are a business owner, investor, or finance professional, understanding IFRS helps you navigate financial statements with greater confidence.
At NAPS, we are committed to equipping future professionals with the knowledge to interpret and apply IFRS effectively. Stay tuned for our next blog, where we will explore Sustainability Accounting—a growing field that integrates environmental and social considerations into financial reporting.
Aflah Tasnim

Easter Breaks in Australia: Tradition, Symbolism, and Social Reflections
Easter is a significant holiday in Australia, widely observed with a mix of religious, cultural, and commercial traditions. For international students, especially those in social work, understanding the historical and social aspects of Easter can provide deeper insight into the cultural landscape of Australian society and its impact on various communities.
The Meaning of Easter and the Holiday Break
Easter, primarily a Christian festival, commemorates the resurrection of Jesus Christ. It is observed on the first Sunday following the first full moon after the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it between late March and April. In Australia, Good Friday and Easter Monday are public holidays, leading to an extended break. This time allows families and communities to gather, reflecting on faith, renewal, and togetherness.
For social work students, Easter presents an opportunity to observe how different community groups engage with the holiday. It is a time when charities and social organisations focus on helping the vulnerable by providing meals, organising events, and addressing social isolation among the elderly or disadvantaged groups.
The Easter Bunny and Eggs: Where Do They Come From?
The Easter Bunny and chocolate eggs have become synonymous with Easter celebrations, but their origins predate Christianity. The rabbit, or hare, is an ancient fertility symbol associated with Eostre, the Anglo-Saxon goddess of spring and renewal. German immigrants brought the tradition of an egg-laying hare (the "Osterhase") to other parts of the world, including Australia. Over time, chocolate manufacturers commercialised the idea, making Easter eggs a beloved tradition.
Eggs, which symbolise new life and rebirth, were originally exchanged and painted in early Christian communities as a representation of Jesus’ resurrection. In modern Australia, this symbolism has evolved into Easter egg hunts, an activity enjoyed by families and communities nationwide.
Easter's Social Implications in Australia
From a social work perspective, Easter highlights various aspects of Australian society, including multicultural inclusion, commercialisation, and social equity. While many enjoy celebrations, others face financial hardship, loneliness, or food insecurity. Organisations such as the Salvation Army and St Vincent de Paul run initiatives to support marginalised communities during this period.
For international students studying social work, Easter offers a chance to participate in community service, observe Australian social structures, and reflect on the importance of cultural traditions in community bonding and support systems. It also serves as an excellent case study of how religious and cultural traditions are adapted within a multicultural society like Australia.
Easter in Australia is more than just a holiday; it is a reflection of history, tradition, and community welfare. Understanding its roots and contemporary impact can provide social work students with a broader perspective on cultural diversity, community support, and the role of social services during national celebrations. Engaging with Easter from a professional and academic viewpoint enables students to appreciate the social fabric of Australia and contribute meaningfully to community well-being.
AI and its Importance to Students in the Professions (Part I)
What is AI?
AI Potential and Fears.
Many experts write of the many positives that AI will bring to almost every field of endeavour. Reflecting upon the immense potential of AI Erik Brynjolfsson and Andrew McAfee wrote in 2018:
Most of the fears about AI are about general AI. At the extremes, some experts think What are the risks to humanity itself when most of the ‘intelligence’ in the world is machine made rather than man-made. The essence of these concerns is captured by world renown theoretical physicist, Stephen Hawking, who noted:
AI Issues for students preparing for a career in the professions.
- Industrial opportunities and challenges in developing AI
- Enhanced data collection, big data analytics/algorithms and ever-increasing application to new areas of human activity.
- Understanding society-wide impact in key areas, eg introduction and rapid expansion in use of automated transport
- Expanding the application of blockchain technology in providing solutions to multiple industries
- The role of AI in the biological sciences and breakthroughs in health informatics
- The role of AI in enhancing the productivity and intellectual power of humans
- Role of humans in interacting with AI products to ensure they are safe and do what we want
- Speech recognition developments to promote universal applications and enhance human-machine interactions
- The impact of AI on digital marketing and other business activities
- Commercialization challenges and opportunities in relation to AI
- Capturing video and incorporating it in AI applications
- Machine and deep learning in the next generation of AI applications
- How to better define and control the boundaries on AI systems
- Growing movement towards singularity and machines approaching and in an increasing number of areas surpassing human intelligence.
- Capturing the potential of big data analytics while at the same time dealing with challenges of discrimination and prejudice that can occur
- How to build AI to Scale and gain return on investment
- Internet of things: use of AI to help build systems in which various technologies are connected and working together to transform organizations and industries.
- The impact of robotics and AI on employment.
- Education: how do we bridge the talent gap needed to develop this important new area? How can universities, through their research mission, better support the growth and development of this important industry? How will AI change how education is delivered and to whom?
- Geopolitical questions such as regulation across national borders, impact on security, cyber warfare and so on
- Challenge of regulation so that AI advances promote industry advancement and at the same time protect important human values such as privacy.
- Law as infrastructure: how can a legal framework be put into place that achieves the benefits of AI while at the same time limiting and guarding against potential harms that may result? How does law, which tends to work on a linear path, keep up with technology which is growing exponentially?
Conclusion
_______________________________